- Objective: Understand the basics of vector graphics and their applications.
- Content:
Bitmap Vs. Vector Graphics
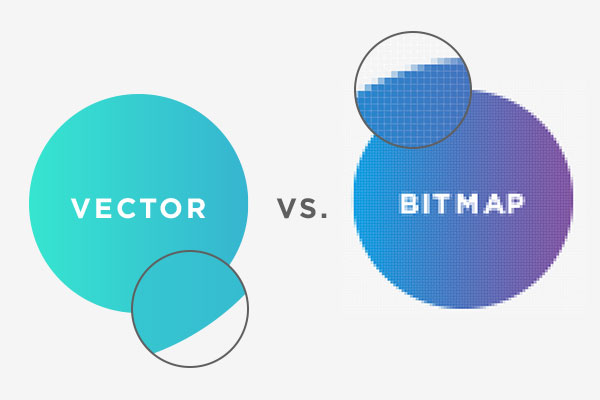
Bitmap or raster graphics are composed of pixels, which are tiny squares of color information arranged in a grid. Bitmaps have a fixed resolution and lose image quality when scaled larger because the pixels become visibly distorted. Vector graphics use mathematical algorithms to calculate and draw points, lines, curves and shapes in images. This allows vectors to scale infinitely without degradation of visual quality or introduction of unwanted pixelation.
Scalability and File Size
The key distinction is that bitmaps have a set pixel dimension, while vectors have no fixed size limitations. Even if a vector image is scaled 1000 times larger, the algorithms reconstruct a sharp, crisp shape. Bitmaps lose clarity when enlarged due to the visibility of individual pixels. Vector images also tend to have drastically smaller file sizes compared to bitmap equivalents, especially photographs. A vector logo may be 5KB whereas a bitmap photo is often 10MB.
Additionally, we can look at a bitmap digital painting transitioning into a vector piece. The bitmap will showcase brush texture and color blending unachievable in clean vector curves. However, the vector will allow the illustration to resize massively without any degradation we'd otherwise see enlarging the bitmap painting. The fundamental stylistic differences achieved through each digital image creation process are further highlighted through these examples.
Common Uses of Vector Graphics
Vector graphics are most commonly used for:
Logos - Branding and logos require images that can be resized across various mediums without losing visual quality. For example, a vector SVG logo retains crisp definition when used on a website, business card, banner ad, billboard, and mobile app.
Illustrations -The smooth lines and curves possible in vectors make them ideal for stylized illustrations, comics, technical diagrams, information graphics, and animated graphics. The ability to separate and manipulate elements also simplifies editing.
Web Graphics - Websites favor vector image files like
SVG and EPS over bitmaps because they load faster and can scale responsively
across device sizes. Vectors allow clean resizing for mobile screens to large
desktop views.
Additionally, vectors are common in graphic design for
print materials, UI design, data visualization, architectural drawings and
mapping. The precision and adaptability make vectors suitable for virtually any
visual output needing dynamic and lossless scaling.
And that wraps up our initial introduction to how vector graphics can help shape designs of the future! This lesson provided a high-level understanding of what constitutes a vector image and how it can be exponentially more adaptable than traditional bitmaps.
The foundation of mathematical manipulation is what
grants vectors their scalable superpowers! In the next lesson, we will dive
deeper into how to harness fundamental points, lines, curves, and primitive
shapes as our building blocks for creating intricate vector illustrations.
So now that you have the basics down for WHAT vectors are and WHY their capabilities are invaluable today, get ready to start learning the applied skills of HOW to orchestrate vectors in action. Get excited to get hands-on with shaping, morphing, and moving vector elements soon! The only limit will be the boundaries of your imagination.
Once you master crafting with primitive vector building blocks, you’ll possess the techniques to craft scalable graphics ready for any design scenario! Expect the foundations provided today to give way to a world of creation possibilities tomorrow when we delve further into practical vector art.


.png)

.png)


0 Comments